

In general, the enhancement in O1 and reduce in O2 within the film causes for the development of c- axis orientation but in this case the increase in O2 peak identifies the. Figure 3 shows the XPS O 1s core-level spectra of the undoped ZnO as well as for nitrogen doped and nitrogen aluminum co-doped zinc oxide lms. ZnO has an unusual O1s spectrum with two peaks possibly indicating either Zn (OH) 2, ZnCO 3. The Strong presence of O2 peak at 500 C justifies the formation of a considerable amount of oxygen vacancies within the Zn lattice interstitials in the ZnO matrix. aluminum co-doped zinc oxide (ZnO:N, Al C N 1:1 wt) lms. The green light emission was strongest and the concentration of oxygen vacancies was highest when the ZnO film was annealed in ambient atmosphere at 900 ☌. Zn2p peak has significantly split spin-orbit components ( metal 23 eV). Under various annealing atmospheres, the analyses of PL indicated that only one emission peak (523 nm) was obtained, indicating that only one class of defect was responsible for the green luminescence.
The PL results demonstrated that the intensity of green light emission at 523 nm also increased with temperature. An analysis of the O 1s peak of ZnO film revealed that the concentration of oxygen vacancies increased with the annealing temperature from 600 ☌ to 900 ☌ under an ambient atmosphere. An analysis of the O 1s peak of ZnO film revealed that the concentration of oxygen vacancies increased with the annealing.
This work demonstrates an advantageous effect of oxygen vacancies on the metal oxide photoanodes during photocathodic protection process.The effects of annealing environment on the luminescence characteristics of ZnO thin films that were deposited on SiO 2/Si substrates by reactive RF magnetron sputtering were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photoluminescence (PL). The effects of annealing environment on the luminescence characteristics of ZnO thin films that were deposited on SiO2/Si substrates by reactive RF magnetron sputtering were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photoluminescence (PL).In a durability test, the photocathodic protection potential further drops and stabilizes at − 930 mV for hours under continuous illumination, which is attributed to the formation of ZnO/ZnS core/shell heterostructures as well as the in-situ creation of anionic vacancies.

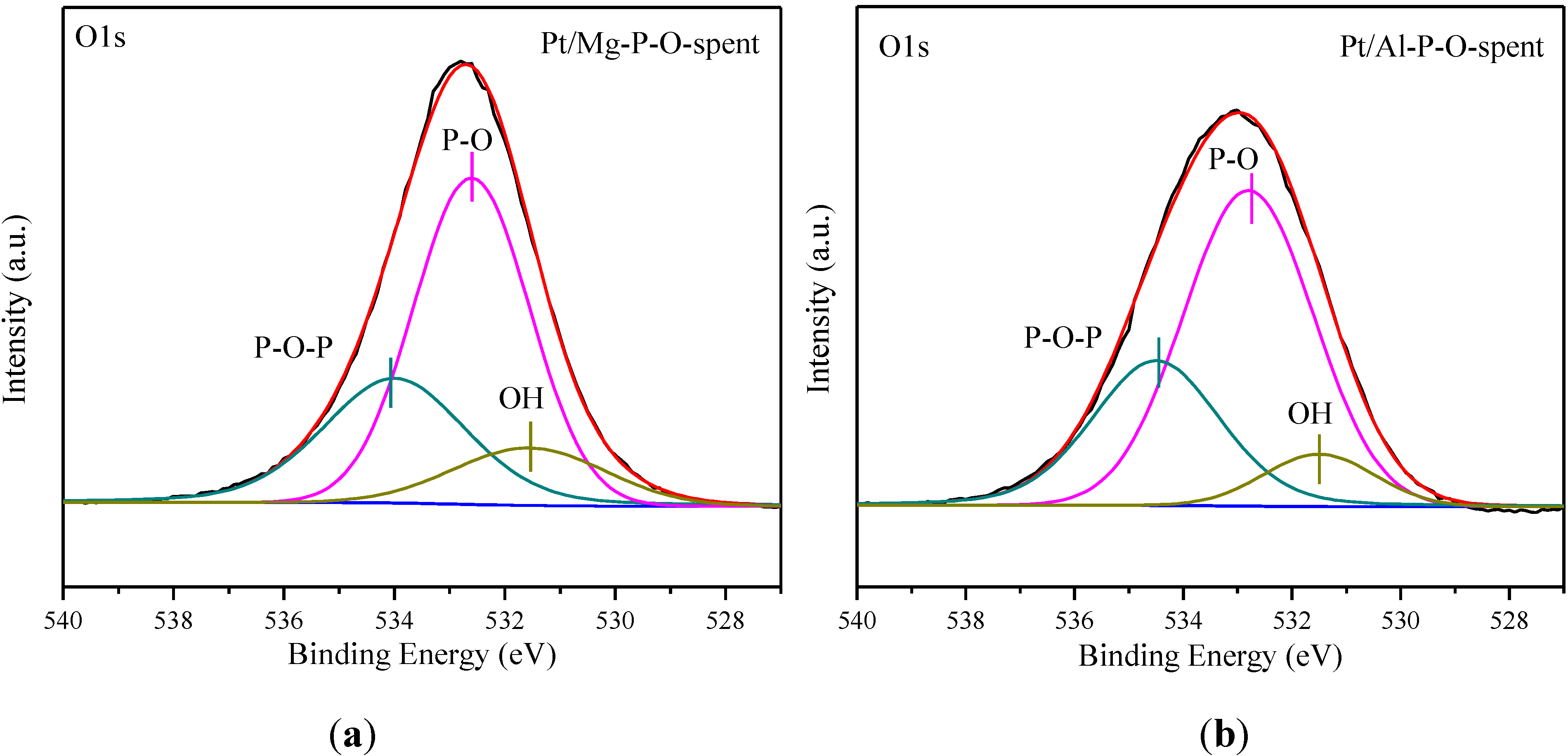
Under intermittent sunlight illumination, the as-prepared ZnO nanowire photoanode shifts the open circuit potential of the coupled 304 stainless steel to − 770 mV with a potential drop of 503 mV relative to steel’s corrosion potential (−267 mV), suggesting a superior photocathodic protection performance. Figure 6a shows XPS spectra of O 1s on the surface of (i). Herein, a robust ZnO nanowire photoanode with an appropriate amount of oxygen vacancies was synthesized through a seed-assistant hydrothermal approach. To calculate the contained of the different dopant concentration in the films and to determinate the chemical state of the film composing elements, XPS analysis was carried out for undoped, 3 Na and 3 K-doped ZnO films, and calibrated according to the C 1s peak at 285 eV. treated ZnO surface had more oxygen vacancies as compared to as-deposited samples.

Oxygen vacancy engineering of metal oxides is an effective strategy to modulate electronic structures and regulate active sites for improving their photoelectrochemical performances.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
